Only 99¢ – Enoch Primordial on Kindle by Brian Godawa.
Chronicles of the Nephilim Biblical Fantasy Saga.http://amzn.to/1mJwHe4
Book Adaptations
This is Why I Have Been Silent Lately

David Ascendant, Book 7 of my Chronicles of the Nephilim is Now Available for Kindle Pre-Order.
Everyone knows the story of David.
Or so you think.
No one has heard it told this way before.
See the Book Trailer, Author Interview, and Cool Art, Then Pre-Order here:
http://bit.ly/1q15gQJ
Deconstructing Noah’s Arc: Godawful Storytelling
I’m the “little guy” who wrote a blog post critiquing an early draft of the Noah script because of my own research into the subject matter. Well, when things went south in the studio screenings of the movie with religious audiences, the blood hound media scoured the internet for negative quotes, found my post, and it went viral.
I thus became Satan for Paramount and its elitist director of dark unsympathetic sick and twisted heroes, Darren Aronofsky.
I finally saw the movie. And now I know why Paramount and its hired Christian marketers would not let me into an early screening to correct my analysis of the early script of Noah.
Because I was right.
Not only that, but the differences between the script and the final movie are so negligible that I won’t have to change a single word of my critique. Just go back and read that and you’ll get the sick twisted agenda that seeps through every frame of this movie.
Wait. I take it back. It’s actually worse than the script.
But right up front, I apologize for giving so much time and attention to preparing people to watch the movie with a thoughtful eye to see what is good first and then describe the bad. Sometimes movies are so bad that what little good in them is so overwhelmed it’s like – well, like being drowned. My problem was I took it too seriously.
The Noah movie is ugly. It’s anti-human exceptionalism. It’s enviro-agitprop. And it’s poorly done. I can’t recommend this movie, not just because of it’s godawful theology (or should I say “earthology”), but because it’s godawful filmmaking. Like The Last Temptation of Christ. All the controversy overshadowed the fact that it was just plain terrible storytelling. Same here.
And people complain about Christian movies being so bad because they are agenda driven while suffering from poor storytelling and preachiness. Well, how about a new term: “Bad atheist movies” that suffer from poor storytelling and preachiness.
I have to say something to all those Christian leaders and film critics who saw the early screenings and kept defending the movie, saying in reference to my viral blog post, “The movie is different, the movie is different. You can’t talk about the movie cause you haven’t seen it.”
Shame on you. Shame on you because you knew when you were saying it, that it wasn’t true and I was right. You were tools. And Aronofsky is laughing at you behind your backs. He’s subverting your sacred story and he’s not even doing it well, but you’re still supporting it. I spoke up for the truth, but you wouldn’t, and you led me like a sheep to the… Okay, maybe I’m not that righteous. I’ve lied before too. As the movie Noah would say, “meat-eating is in all of us” or something like that.
Was Anything in it Good?
Well, uh… the movie captures a visual picture of the Flood that has never before been captured. That’s cool. Bursting waters, a Doré homage of people on a mountaintop being pulled into the rising waters. Okay, Flannel graph successfully overthrown. I liked that.
Oh, and uh people are shown as really evil so they deserved to die. That’s true. (Even though the evil is really more about meat-eating than anything else.)
Ummm.
Okay, now I want to talk about what I didn’t like about it.
“On the nose” dialogue. Flat characters that you just don’t care about. A sick twisted hero that you just don’t care about. Look, I know your hero has to have a character flaw, but this is so extreme that you can’t stand Noah, and you just want to leave the theater.
Noah becomes so convinced that the wickedness of man is in everyone (that is the original sin of being bad to animals and the earth – and did I say meat-eating, you carnivores?) that they all deserve to die, including his family — and then Noah becomes obsessed with killing his newborn granddaughters on the ark. Of course he doesn’t. That’s good. Whew. Not. Good. Enough.
Aronofsky gave us his “brilliant” portrayals of sick twisted drug addicts, sick twisted wrestlers, and sick twisted ballerinas. And now, in a fit of creative originality, a sick twisted Noah! Do you think maybe there’s a pattern here that might say something more about Aronofsky than anything else?
The fact that Noah wrestles with justice and mercy through the story is a good thematic idea. Justice without mercy is cruelty, but mercy without justice is also cruelty. But as Aronofsky said in an interview Noah’s journey is God’s journey of being so judgmental that he has to learn mercy. Because you see, Aronofsky has said he is a humanist. Humanists believe man is the measure of all things and man is not created in God’s image, God is created in man’s image. So it makes sense within his atheism to portray God as learning to be more merciful since God is merely an extension of man’s own imagination.
Remember when I said the script has Noah as a humanist who is more compassionate than God because he just can’t bring himself to kill his family like God wanted him to? Still in there. Yep.
Cliché stereotypical bad guy. Now whenever you want to know who a storyteller hates, look at his bad guy’s belief system and rationale and you’ll find a comparison to a modern day counterpart. Okay, so Tubal-cain is the bad guy. He is an urban “industrialist” (the movie calls the cities, “industrial”) who mines the earth for resources, claims property rights to owning land, hunts animals, eats meat, uses a primitive gun (I’m not kidding you, he probably got it from ancient aliens), he keeps emphasizing that man is created in the image of God and superior to the animals, and that we are supposed to subdue them and have dominion over them. All this while he rapes, murders, pillages and eats meat. So that kind of thinking is supposed to lead to that kind of evil behavior, got it? Sooooo, let’s see, who are those in todays’ world that believe in industry, mining for energy, private property rights, in hunting, guns, and say that God created man in his image to have dominion. Tubal–cain is basically an evil caricature of Judeo-Christian Western civilization. Seeing behind the shallow stereotype of evil reveals as much about the storyteller’s perception of what worldview he considers leads to such evil.
Christians, you are tools being played if you think that this movie is anything BUT a subversion of the Biblical God and an exaltation of environmentalism and animal rights against humans. Those who say that hurting the earth is just part of the sins of mankind in the story are missing the deeper point. No matter what “sins” of man that are portrayed in this story, they are only expressions of the ultimate sin, which is to sin against the earth. Every time it talks about man’s sin and God’s intent, the context is always “creation” not God, and not man as God’s image. The guy who preaches “man as God’s image” is the villain. “Creation” as in “Nature” is the metanarrative here, NOT God.
For those of you Christians who are fooling yourselves, just ask yourself this: Does Aronofsky believe in the God of the Bible as holy or in the earth as holy? I think you know the answer. And it ain’t both.
The very first thing said and repeated later is “In the beginning, there was nothing.” Now folks, Aronofsky is an atheist. He is subverting your Creation narrative that says “In the Beginning God…” not “Nothing.” Atheism believes that everything came out of nothing. And they say Creationists believe in irrational anti-science fairy tales!
Even in the end, Aronofsky’s humanism subverts God when Noah has his revelation about God’s purpose. Why didn’t God tell him whether or not to kill those little granddaughters so that the human race would never again corrupt Mother Earth? He kept asking, but God was silent. His daughter-in-law tells him “because he wanted you to decide if man was worth saving.” You see, it’s all up to man. God is not the one to decide if man is worth saving, MAN is. Because of course, in Aronofsky’s humanistic atheistic universe, God is only a belief, not a real being, and man must make the ultimate decisions of value and dignity.
Well, I say no thank you Mr. Atheist. That leads to guillotines, gulags, and gas chambers – which were all spearheaded by ATHEISTS.
Aronofsky has hijacked the Biblical narrative and subverted it to preach his secular humanistic atheist enviro-worship. He said himself that the story is just a myth that he turned into a prop for environmentalism. But its not even good preaching. It’s cheesy atheist preaching.
I found it telling that the movie that stresses so much about how bad meat-eating is, would fail to include the fact that God himself killed animals to clothe Adam and Eve, and that righteous Abel sacrificed animals as worship to God. He was after all, a shepherd of herds. And lastly that regardless of any alleged vegetarianism before the Flood, God decreed after the Flood that all living things were good for man – to – EAT! In the Bible, Noah was a member of PETA all right: People Eating Tasty Animals. But of course, that doesn’t fit the environmentalist/animal rights agenda. THAT God is evil to them. But you can see where all the attacks against Christians for nitpicking “unbiblical details” is not an entirely fair accusation. Because sometimes, those details are changed because the director is subverting the story to spin it to his ideological agenda against the text.
I heard Mr. Aronofsky is a vegan. He better be, after watching the hate fest against meat-eating in this movie. I’d like to invite him over to an animal rights barbecue to discuss the moral and intellectual impoverishment of atheistic humanism. And I would love to learn how he powered that movie set and production with solar and wind power. Must have been a real miracle. Oh, you mean he burned fossil fuels to make the movie, just like Tubal-cain? Oh, that’s right; Celebrities get a Green pass for their conspicuously Nephilim-sized carbon footprints.
But the topper has got to be the Rock People. They are supposed to be the Watchers that fell from heaven and took on cooled magma as their bodies, and now they are helping Noah. But they look like goofy ancient Transformers who, instead of transforming into cool cars and trucks, just transform into – well, rocks. They completely make you suspend your suspension of disbelief because they are so goofy. Remember Jar Jar Binks? Yep, that bad. I won’t even go into how wrong Aronofsky got the Watchers, which were bad guys in the Biblical and Jewish legends, but he makes them good guys! But that’s in my earlier critique.
The special effects, from the weak opening graphics to the alien-like luminescent bodies of Adam and Eve, to the most unscary serpent I have ever seen in a movie, to the silly looking large Rock People, the visual imagery is that of a B-grade movie. Where did that $130 million go? To Solyndra and Al Gore? You watch the movie asking yourself, is the director trying to make some kind of “artistic statement” by using cheap looking special effects? Or is he just so used to making low budget movies that he doesn’t know how to do it any better?
But in the end, Noah does realize his extremism was all wrong and that he should “be fruitful and multiply and replenish the earth.” So maybe I’ve got it all wrong. Maybe Aronofsky is a crypto-Christian who is secretly trying to show that atheist environmentalism is obviously insane and immoral and leads to murdering humans in the name of compassion to animals and the earth.
Or maybe, like today’s environmentalist anti-human exceptionalism, he cannot see the irrational contradictions of his own beliefs that deconstruct.
At least Avatar, with its naked pagan earth worship, has a ring of more authenticity than trying to subvert someone else’s sacred narrative with silly rock people and bad guys who cling to their guns and eat meat. But also because Avatar is just a well made pagan movie.
Noah is a poorly made atheist movie. Noah tanks.
P.S. I am not now, nor have I ever been a card carrying member of the oil company cartel.

The Noah Movie: How To Watch It with Wisdom and Discernment

In my last post, I addressed the issue of concern that some religious believers have about whether or not to see the new movie Noah by atheist director Darren Aronofsky. I explained that there was merit in both arguments to see or not to see the movie. I concluded that if you were not sure whether you wanted to see it or not, I will be blogging my own analysis of the movie after it opens on March 28. Or you can read other reviewers you respect before you make your decision.
I’m the Hollywood screenwriter and novelist who wrote the blog analyzing an early script of Noah that went viral. It was quoted by all the news outlets, mostly for its negative comments while ignoring the positive ones.
Why did I do it? Because I LOVE movies, and I see their potential for both good and bad influence on our cultural values. That’s why I wrote Hollywood Worldviews: Watching Films With Wisdom and Discernment. To help people decide for themselves what values and meanings they are ingesting in their media consumption.
But I’ve also studied the story of Noah for many years, wrote an Amazon category bestselling novel called Noah Primeval, and set up a website, www.noahprimeval.com for all things Noah. My fans want to know about these things, and so do I.
Things To Look For
Most movies are a mixture of good and bad. But discerning that difference can be difficult without a more informed approach to understanding how storytelling and film embodies worldviews and meaning. So, if you’ve decided to watch the movie, I wanted to offer up some ideas to keep in the forefront of your mind as you watch. These will help you understand and appreciate what you like about the movie and be able to discern what you may not like about it for your discussion with others.
Have Some Tolerance For Creative License And Fantasy In The Story
Some hyper-literalists are already complaining that the movie doesn’t follow the details of the Bible. But some of those details are either not relevant or subject to differing interpretation. So chill out.
Take for instance, one example some have talked about. The Bible says that “eight persons were brought safely through water” (1 Peter 3:20). That is, Noah, his wife and three sons, and their three wives. But some hyper-literalists have yelped that in the movie, only six people are in Noah’s family on the ark. Two wives are missing.
The problem with this criticism is its lack of imagination. We find out that one of the daughters is pregnant with twins, which will be the two wives of the other two sons. So, if you are a Pro-Life Christian, then you have to acknowledge that that is technically the eight persons on board, including the four wives. Unless you want to deny the humanity and personhood of the unborn.
Watch The Hero’s Character Arc (not Ark)
The details that really do matter are the ones that reflect the meaning or worldview of the story. And those can be found in paying close attention to the hero’s journey. In storytelling, the hero’s journey is the incarnation of the meaning of the story.
The hero starts out as someone we root for and so we learn to see the world through his eyes by our identifying in sympathy with him. But the hero has an inner flaw, something wrong about the way he sees the world. This flaw results in him making some bad choices. So even though he is sympathetic, we still see he has a goal that he pursues for flawed reasons. As he pursues that goal, he is blocked by obstacle after obstacle, including the villain, that thwarts him at every turn.
The story builds until the point where the hero appears that he will never achieve his goal. When all hope is lost, he faces the truth about himself and gains the inner understanding of his flaw that allows him to achieve what he really needs instead of what he wants. He then embraces this truth, changes and finds the strength to do the right thing at the end. This is the redemption of the hero.
What Is The Hero’s Character Arc In Noah?
Noah was a righteous man of faith. But he was not sinless like Jesus Christ. Noah was a sinner, and therefore had character flaws. The Bible reveals Noah’s drunkenness after the Flood for instance (Genesis 9:21).
So look for Noah’s character flaw in the story and you will understand the meaning that the storyteller is conveying through the hero’s discovery of that flaw. What Noah learns by the end of the film is the moral premise of the story.
How does Noah see the world in the beginning of the story?
As the story moves, what is apparently wrong about the way that Noah sees the world?
What is the villain’s motivation for fighting Noah? This will be the worldview that the storyteller is trying to criticize as wrong or evil.
What is the catalyst that helps Noah to see he is wrong near the end of the story?
How does he change his view about the world or himself and why?
What does he do differently at the end to show a changed life?
The problem with some movies is how dark and unsympathetic the heroes can be. Ask yourself is Noah’s flaw too extreme? Does it make him unsympathetic to you? Why or why not?
That is how the storyteller influences us to see the world through the eyes of the hero with whom we sympathize or identify with.
Bonus Questions About God
God is a tough character to depict in film. Too direct and it seems cheesy, too indirect and it seems like God could be the delusions or dreams of a religious nut.
How is God depicted in the movie?
Does he have a real presence or is he depicted more as a belief that could be explained as self-made dreams or delusions?
Why is God ultimately judging the world? Many sins will surely be depicted, but is man’s sin against God the primary reason or is it man’s “misuse” of the environment?
Since Aronofsky is an atheist and does not believe man is created in God’s image, but rather that God is created in man’s image, how do you think that worldview informs his take on the sacred story of Noah?
Brian Godawa. Hollywood screenwriter and author of the Amazon bestselling novel, Noah Primeval, a Biblical fantasy with creative license that retells the Noah story without a modern secular or environmentalist agenda.
The Noah Movie: To See or Not To See?
With all the controversy surrounding the new Noah movie, many Christians, Jews, and Muslims are wondering whether they should go see the movie that was directed by atheist Darren Aronofsky and stars Russell Crowe in the lead role as the sacred mariner.
On the one side are the cultural anorexics who demand that a movie about the Bible should follow every jot and tittle detail from the Bible as they interpret it, without any creative license. They tend to yell “boycott!” and seem so hyper-literal in their views that they often miss the deeper poetic meaning of much figurative language in Scripture.
On the other side are the cultural gluttons who tell religious believers to shut up and go see the movie, and be happy with what Hollywood gives us instead of complaining. They tend to lump all criticism into the “angry reactionary Christian” stereotype and seem to be more against their own spiritual family members than the world that rejects their Savior.
I feel like I’m in between those two extremes. I’m the Hollywood screenwriter and novelist who wrote the blog analyzing an early script of Noah that went viral. It was quoted by all the news outlets, mostly for its negative comments while ignoring the positive ones.
Why did I do it? Because I LOVE movies, and I see their potential for both good and bad influence on our cultural values. That’s why I wrote Hollywood Worldviews: Watching Films With Wisdom and Discernment. To help people decide for themselves what values and meanings they are ingesting in their media consumption.
But I’ve also studied the story of Noah for many years, wrote an Amazon category bestselling novel called Noah Primeval, and set up a website, www.noahprimeval.com for all things Noah. My fans want to know about these things, and so do I.
To See or Not To See?
On the one hand, there is the argument that we should not give our money to Hollywood studios who will only be encouraged to make more movies that twist our sacred stories unless they listen more carefully to their audiences. It seems Christians are the only politically correct victims that are still acceptable to villainize in the media. These Christians supported The Passion of the Christ and Son of God, but they question Noah and the upcoming Exodus movie by atheist director Ridley Scott. They are not the intolerant bigots that some want to make them out to be. They care about their sacred story being subverted into a secular worldview. That is a legitimate concern.
But on the other hand, I also understand the argument that this movie is an opportunity to engage with the culture. Good or bad movie that it will be, Noah is opening the discussion about a topic that is normally ignored or scoffed at in our culture. This is a Gospel opportunity like never before. Christians can and should seize the moment to talk about the God of Noah who rescues us through the ark of Jesus Christ from our sins.
Now, you can’t very well talk intelligently about a movie you haven’t seen. People won’t respect your view if you haven’t. But if you have seen it, then you can show people how actually open-minded Christians are by saying what you liked and did not like about the movie. After all, no movie is all bad or all good. Most are mixed bags of good and bad. You can explain where you think the movie diverts from the Bible. You can encourage them to read the original story, since everyone knows the book is usually better than the movie (Except for Forrest Gump and the Godfather). And you can do so respectfully and with a winsome attitude of tolerance that atheists usually do not have for you.
I will be seeing it because I am a screenwriter and blogger about movies to help forward the conversation about the worldviews and meanings of movies. And of course, I have my own Noah Primeval novel and website, so my fans want to know. Plus, I don’t have to agree with everything in a movie to appreciate what is good in it.
So my advice is that if you really don’t trust Hollywood or are not sure you do in this particular case, then keep an eye on my Movieblog, because I will be writing a review on the opening release date of the movie with my analysis. Until then, I can’t recommend or not recommend a movie because I haven’t seen it.
If you do want to see the movie, then on the next post, I will give advice on the kind of things to look for when watching a movie to determine the worldview and values it is espousing through the art of storytelling. It’s not always obvious, but it is always there.
Brian Godawa. Hollywood screenwriter and author of the Amazon bestselling novel, Noah Primeval.
Noah Facts #10: The Book of Enoch, Watchers and Giants
With all the talk about the movie Noah starring Russell Crowe, I thought I would add to the conversation so you can be prepared to watch the movie with wisdom and discernment.
I’ve written a Biblical fantasy novel called Noah Primeval. I’ve researched this topic extensively. Noah Primeval has been a category bestseller on Amazon for 3 years. It’s first in a series of novels called Chronicles of the Nephilim.
The Fascinating Case of the Book of Enoch
One of the most fascinating cases of Biblical appropriation of non-canonical texts is the New Testament references to the book of 1 Enoch. Written sometime around the third to second century B.C., this text has both haunted and been cherished by the Christian Church through its history. It is apocalyptic in genre; cloaking warnings of judgment in dream visions, parables, and complex allegorical imagery. But it is most well-known for its detailed elaboration of the Genesis 6 story about the Sons of God (called “Watchers”) and their intimate involvement in the cause of the Noachian Flood.
There it describes in much detail the Watchers as fallen angels revealing occultic secrets to mankind, having intercourse with human women, and birthing giants who cause terror across the land. (1) Here is just a sample of passages that tell that story in much more vivid detail than Genesis 6:
Enoch 6:1-2
In those days, when the children of man had multiplied, it happened that there were born unto them handsome and beautiful daughters. And the angels, the children of heaven, [the Watchers] saw them and desired them; and they said to one another, “Come, let us choose wives for ourselves from among the daughters of man and beget us children.”
Enoch 7:1-8:3, 19:1
And they took wives unto themselves, and everyone respectively chose one woman for himself, and they began to go unto them… And the women became pregnant and gave birth to great giants.
These giants consumed the produce of all the people until the people detested feeding them. So the giants turned against the people in order to eat them. And they began to sin against birds, wild beasts, reptiles, and fish. And their flesh was devoured the one by the other, and they drank blood. And then the earth brought an accusation against the oppressors.
And Azaz’el [the Watcher] taught the people the art of making swords and knives, and shields, and breastplates… and alchemy…[or transmutation: Ancient Ethiopian commentators explain this phrase as “changing a man into a horse or mule or vice versa, or transferring an embryo from one womb to another.”] Amasras taught incantation and the cutting of roots; and Armaros the resolving of incantations; and Baraqiyal astrology, and Kokarer’el the knowledge of the signs, and Tam’el taught the seeing of the stars…
The angels which have united themselves with women. They have defiled the people and will lead them into error so that they will offer sacrifices to the demons as unto gods.
Enoch 10:4, 11-12; 54:6
the Lord said to Raphael, “Bind Azaz’el hand and foot and throw him into the darkness!” And he made a hole in the desert which was in Duda’el and cast him there…And to Michael [the archangel] God said, “Make known to Semyaza [the Watcher] and the others who are with him, who fornicated with the women, that they will die together with them in all their defilement…bind them for seventy generations underneath the rocks of the ground until the day of their judgment and of their consummation, until the eternal judgment is concluded… on account of their oppressive deeds which (they performed) as messengers of Satan, leading astray those who dwell upon the earth.” (2)
Though 1 Enoch is not in the Western canon of Scriptures, it is in the Eastern Ethiopic canon, and was respected by Christian scholars and authorities throughout the early church. It was never considered heretical by church authorities.
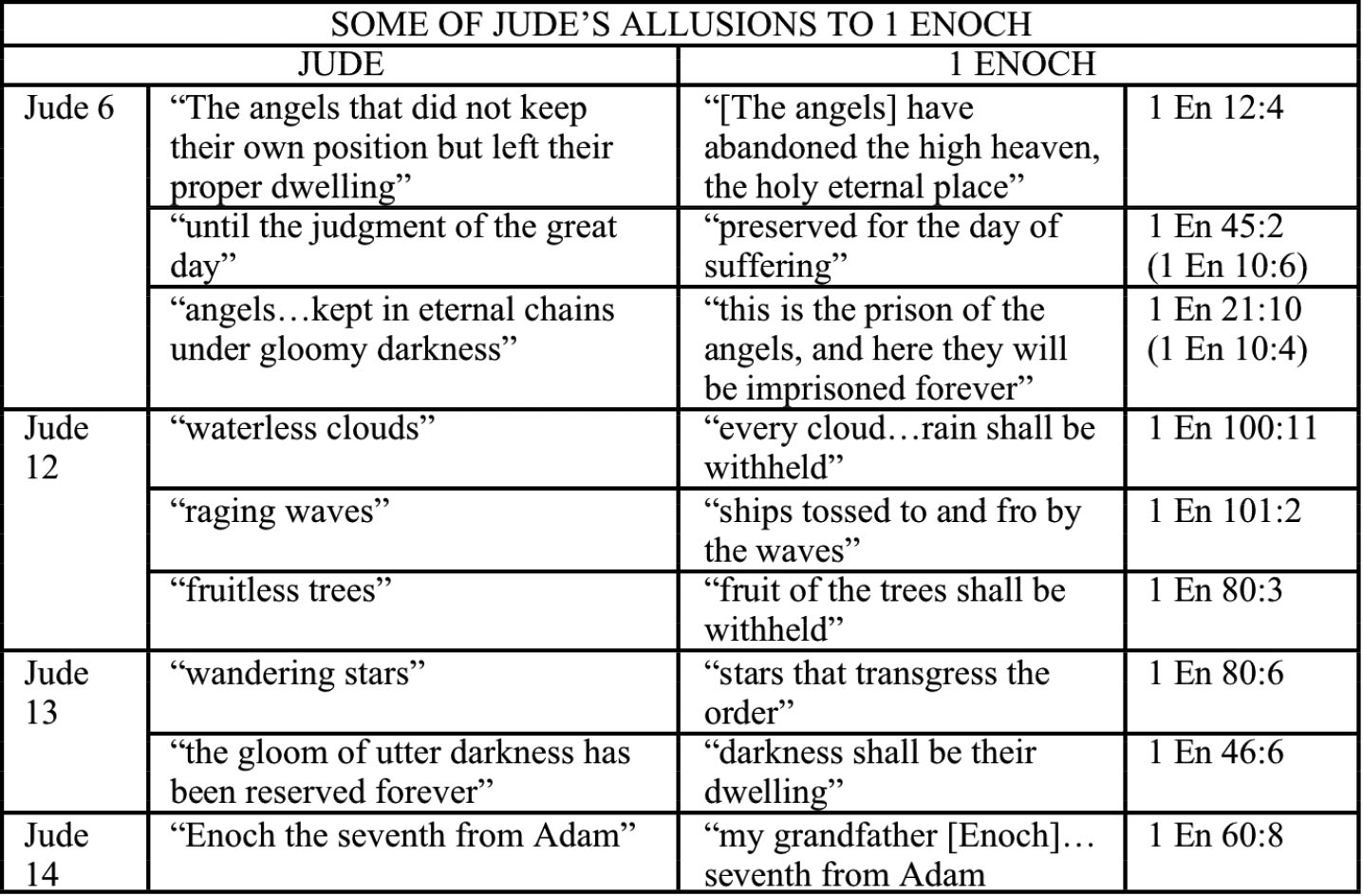
But the real kicker is that the New Testament even refers favorably to the book of Enoch and its tradition of fallen angels cohabiting with humans which results in their punishment of binding (1Pet. 3:19-20; 2Pet. 2:4-10; Jude 6-14).
First, Jude quotes the book of 1 Enoch outright when he writes of false teachers corrupting the church:
Jude 14-15
It was also about these that Enoch, the seventh from Adam, prophesied, saying, “Behold, the Lord comes with ten thousands of his holy ones, to execute judgment on all and to convict all the ungodly of all their deeds of ungodliness that they have committed in such an ungodly way, and of all the harsh things that ungodly sinners have spoken against him.”
Here is the text from the actual book of 1 Enoch that Jude is quoting:
1 Enoch 1:9
“And behold! He cometh with ten thousands of His holy ones to execute judgement upon all, and to destroy all the ungodly: And to convict all flesh of all the works of their ungodliness which they have ungodly committed, and of all the hard things which ungodly sinners have spoken against Him.” (3)
But not only does Jude explicitly quote a passage out of 1 Enoch regarding God coming with the judgment of his divine council of holy ones (Sons of God), but all three texts refer to the Enochian notion of the angelic Watchers’ punishment for co-habiting with humans as a violation of the divine/human separation; another main theme of 1 Enoch.
1Pet. 3:18–20
[Christ], being put to death in the flesh but made alive in the spirit, in which he went and proclaimed to the spirits in prison, because they formerly did not obey, when God’s patience waited in the days of Noah.
Jude 6-7
And angels who did not keep their own domain, but abandoned their proper abode, He has kept in eternal bonds under darkness for the judgment of the great day, just as Sodom and Gomorrah and the cities around them, since they in the same way as these indulged in gross immorality and went after strange flesh, are exhibited as an example in undergoing the punishment of eternal fire.
2Pet. 2:4-10
For if God did not spare angels when they sinned, but cast them into hell [Tartarus] and committed them to pits of darkness, reserved for judgment; and did not spare the ancient world, but preserved Noah…and if He condemned the cities of Sodom and Gomorrah to destruction by reducing them to ashes, having made them an example to those who would live ungodly lives thereafter… then the Lord knows how to…keep the unrighteous under punishment for the day of judgment, and especially those who indulge the flesh in its corrupt desires and despise authority.
The New Testament literary reference to non-canonical sources does not mean those sources are the inspired Word of God, nor that everything in them is true; but it certainly does illustrate that the Bible itself draws meaningfully and favorably from interpretive traditions that engage in imaginative embellishment of Biblical stories. Unlike some Christians, God does appreciate creative imagination.
Jude’s references to the book of Enoch are not limited to material citations. He uses the same poetic phraseology throughout his letter that indicates an intimate interaction with the entirety of 1 Enoch on the incident of the Watchers and their condemnation. Researcher Douglas Van Dorn has put together a helpful chart of these linguistic comparisons. (4)
1 Peter 3:18-20 speaks of Christ going down into Hades to proclaim his triumph to the “spirits imprisoned” at the time of the flood. This act appears to be a typological replay of Enoch’s own vision journey into Hades to see the “prison house of the angels” who disobeyed at the flood (1 Enoch 21:9-10).
But the story does not yet end there. You will notice that the location of punishment and binding of the fallen angels that we have already seen in 2 Peter is Tartarus in the Greek.
2Pet. 2:4
For if God did not spare angels when they sinned, but cast them into hell [tartarus] and committed them to pits of darkness, reserved for judgment.
What is important to realize is that the Greek word translated as “hell” in this English translation is not one of the usual New Testament Greek words for hell, gehenna or hades, but tartarus.
Readers may be familiar with the Greek myth of Tartarus as the place where the Titans were imprisoned by the gods. Obviously, Peter does not affirm Greco-Roman polytheism by referring to Tartarus, but he is alluding to a Hellenistic myth that his readers, believer and unbeliever alike, would be very familiar with, subverting it with the Jewish traditional interpretation.
Extrabiblical Second Temple Jewish legends connected this legend of gods and bound Titans in Tartarus to the bound angelic Watchers and punished giants of Genesis 6.
Sibylline Oracles 1:97-104, 119
enterprising Watchers, who received this appellation because they had a sleepless mind in their hearts and an insatiable personality. They were mighty, of great form, but nevertheless they went under the dread house of Tartarus guarded by unbreakable bonds, to make retribution, to Gehenna of terrible, raging, undying fire…draping them around with great Tartarus, under the base of the earth. (5)
Other well-known Second Temple literature reiterated this binding in the heart of the earth until judgment day:
Jubilees 4:22; 5:10
And he wrote everything, and bore witness to the Watchers, the ones who sinned with the daughters of men because they began to mingle themselves with the daughters of men so that they might be polluted…
And subsequently they [the Watchers] were bound in the depths of the earth forever, until the day of great judgment in order for judgment to be executed upon all of those who corrupted their ways and their deeds before the LORD. (6)
This “binding” or imprisoning of supernatural beings in the earth is expressed in 2 Peter’s “cast into pits of darkness reserved for judgment” (3:19), 1 Peter’s “disobedient spirits in prison” (v. 6), and Jude’s “eternal bonds under darkness for the judgment of the great day” (2:4).
Yes, indeed, the New Testament does use 1 Enoch as a source for its own canonical writings. The preponderance of evidence shows that not only does the New Testament letter of Jude quote directly from 1 Enoch 1 (Book of the Watchers), but the entire letter and its alternate version in 2 Peter, show signs of literary and theological dependency on the rest of the Book of the Watchers (Chaps. 1-36), as well as chapter 80 (Book of Luminaries), chapter 46 (Book of Parables), and chapter 100 (Epistle of Enoch). 2 Peter shows evidence of structural and thematic dependency on 1 Enoch 17-22 and 108 (Additional Books). But the fact is, the entire New Testament shows such a multitude of allusions and linguistic echoes of the entire corpus of 1 Enoch, that one can safely say, the book and its basic interpretations may not be Scripture, but are surely legitimated by the Bible and are therefore worthy of study and high regard by the Christian Church.
FOOTNOTES
1. 1 Enoch chapters 1-36 is called the “Book of the Watchers” and deals with this material. The book of Jubilees is another respected text that contains a detailed retelling of the Noah story with Watchers cohabiting with women, and birthing giants. See Jubilees 4-10 and 20:4-5.
2. James H. Charlesworth, The Old Testament Pseudepigrapha: Volume 1, (New York; London: Yale University Press, 1983) 16-18, 38.
3. Pseudepigrapha of the Old Testament, ed. Robert Henry Charles, Enoch 1:9 (Bellingham, WA: Logos Research Systems, Inc., 2004) 14.
4. Douglas Van Dorn, (2013-01-21). Giants: Sons of the Gods (Kindle Location 4850). Waters of Creation. Kindle Edition.
5. James H. Charlesworth, The Old Testament Pseudepigrapha: Volume 1 (New York; London: Yale University Press, 1983), 337.
6. James H. Charlesworth, The Old Testament Pseudepigrapha and the New Testament, Volume 2: Expansions of the “Old Testament” and Legends, Wisdom, and Philosophical Literature, Prayers, Psalms and Odes, Fragments of Lost Judeo-Hellenistic Works (New Haven; London: Yale University Press, 1985), 62, 65.
Noah Facts #9: Round 2 – Noah Vs. Gilgamesh Smackdown!

Noah is a hot topic these days because of the movie with Russell Crowe. Here is some research I’ve done to add to that conversation.
I’ve written a Biblical fantasy novel called Noah Primeval. I’ve researched this topic extensively. Noah Primeval has been a category bestseller on Amazon for 3 years. It’s first in a series of novels called Chronicles of the Nephilim.
Down and Dirty Comparison of Genesis with Gilgamesh
In the previous post, I introduced the issue of the Epic of Gilgamesh and it’s parallel with the Noah story in Genesis. Now, let’s take a closer look.
Biblical scholar Gordon Wenham has listed seventeen major correlations between the Genesis Flood and the Gilgamesh Deluge that indicate a strong genetic connection between the two narratives:
1. Divine decision to destroy
2. Warning to flood hero
3. Command to build ark
4. Hero’s obedience
5. Command to enter
6. Entry
7. Closing door
8. Description of flood
9. Destruction of life
10. End of rain, etc.
11. Ark grounding on mountain
12. Hero opens window
13. Birds’ reconnaissance
14. Exit
15. Sacrifice
16. Divine smelling of sacrifice
17. Blessing on flood hero (1)
These similar details clearly show a common source connection. From where, it is not certain. But Alexander Heidel’s classic The Gilgamesh Epic and Old Testament Parallels has teased out the differences between the two that shed light on their radically divergent meanings regarding the cause of the Flood and the possibility of redemption for humanity. (2)
In Gilgamesh, the gods send the Deluge because of an undefined sin of mankind (Tablet XI:180). Utnapishtim lies to his neighbors about the ark because the gods do not want man to know what they are about to do.
Contrarily, in Genesis, the Flood is very clearly a righteous judgment upon an earth that was “corrupted and filled with violence.” “The LORD saw that the wickedness of man was great in the earth, and that every intention of the thoughts of his heart was only evil continually.”
God gives man a “period of grace” of one hundred and twenty years with which to repent and obey God (Gen 6:5-6). Though this purpose is not stated explicitly in Genesis, another passage in the New Testament seems to indicate this notion of God providing such opportunity.
1 Peter 3:19–20
[In the spirit] he went and proclaimed to the spirits in prison, because they formerly did not obey, when God’s patience waited in the days of Noah, while the ark was being prepared, in which a few, that is, eight persons, were brought safely through water.
Surely, there is an assumption, sometimes explicit, but always implicit throughout the Old Testament that if man repents, God will stay his hand of planned judgment.
The ark also provides an example of significant difference between the narratives. The length of Noah’s ark was 450 feet long, 75 feet wide, and 45 feet high, with a displacement of approximately 43,300 tons. It had three levels to contain the animals, that on the surface of the account is structurally feasible.
Utnapishtim’s vessel however, was not so amiable to reality. According to Babylonian measurements, it was supposed to be a square cube of 200 feet on all sides and was divided into seven levels, displacing approximately 228,500 tons, making it a rather questionable sea worthy craft. (3)
In the Biblical story, it is well known that the flood began with rain coming down from the heavens and waters coming up from the deep. The rain storm lasted 40 days and 40 nights, and then after 150 days, the waters began to abate until the earth was dry enough to leave the ark about 360 days or 1 year after the start of the flood.
In the Babylonian versions, the flood storm lasts only 7 days and 7 nights, followed by an unspecified number of days for the waters to dry up before Noah leaves the ark.
Upon leaving the boat, Utnapishtim and Noah both build altars and offer sacrifices of thanksgiving and appeasement unto their gods. But the theological incongruity between the accounts is spelled out in the divine reactions.
In Gilgamesh, “The gods smelled the savour, the gods smelled the sweet savour, the gods gathered like flies around the sacrificer” (Tablet XI:161-163). Of this passage, Andrew George writes,
The simile used to describe the gods’ arrival is famously the image of hungry flies buzzing around a piece of food. This imagery implies a somewhat cynical view of gods, even more disrespectful than the earlier simile likening them to cowering dogs. (4)
Enlil then starts to quarrel with Enki for revealing the secret to Utnapishtim, wherein Enki defends himself with trickery by arguing that he did not reveal it directly to Utnapishtim, but through a dream, thus freeing him from blame.
Contrary to the Babylonian zoomorphic simile of the gods, the Bible engages in anthropomorphism (human-like) in that man is created in the image of God and thus sacrifice is understood in the priestly terms of atonement for sin (Lev. 1:9). God “smelled the pleasing aroma, the LORD said in his heart, ‘I will never again curse the ground because of man (Gen. 8:21).’” Heidel explains
The propitiatory character of the sacrifice is brought out quite clearly in the biblical narrative, where the ascending essence of the burnt-offerings is called a “soothing odor,” or, literally, an “odor of tranquilization.” One purpose of Noah’s sacrifice, as seems to be indicated by what follows, probably was to appease the wrath of God which had been kindled by the sins of mankind and which Noah had just witnessed. But at the same time it was undoubtedly an offering for the expiation of his own sins and those of his family. (5)
Whereas the Babylonian anthropomorphic descriptions of their deities tended to reflect human weaknesses (hunger) and sin (quarreling), the Biblical account depicts the human-like character traits of God in terms of relationship (propitiation and atonement).
In the Babylonian versions, Noah and his wife are blessed with eternal life after Enlil gives in to Enki’s defensive arguments. They are then taken to a distant place, “at the mouth of the rivers,” probably referring to the Persian Gulf, into which the Euphrates and Tigris rivers opened up.
The Biblical version is theologically motivated by God’s covenantal nature. God blesses Noah, and then grants him the original charge given to Adam to multiply and fill the earth, and to exercise dominion over the creatures (Gen 9:1-3). As the flood was a return to the chaos waters before creation, so the world of Noah is a new creation with a new Adam. And God reinforces his value of the created image of God in man, by bringing special attention to capital punishment for murdering man, made in the image of God.
The rainbow becomes God’s covenant promise to stay his hand from Deluge judgment, unlike the Gilgamesh Epic, that has a secondary mother goddess claim that a necklace strung with flies will, “remind her of the hungry gods buzzing around [Utnapishtim’s] sacrifice, and ultimately of her special responsibility to her human children” (6)(Tablet XI:165-169).
Comparison and Contrast
The value of comparative religion lies in achieving a better understanding of the historical and cultural context of ancient writings like the Bible. Too often, both religious believers and unbelievers approach the text with their own preconceived modern worldview or political agenda that they project upon the text in order to “use” it for their own purposes, positive or negative.
Christians have been guilty of forcing poetic passages into the straightjacket of a hyper-literalistic hermeneutic, or imposing our notions of historical accounting or scientific accuracy upon ancient writers who just did not write with our post-Enlightenment modern scientific or historical worldview.
But it works the other way as well. Modern notions of literary evolution get imposed upon the Bible by detractors who wish to discredit the narrative by reducing it to one of a variety of myths that evolve over time. This modern prejudice also ignores the polemical thrust of much ancient literature that interpreted historical events with divergent meanings, or engaged in retelling narratives through contrary theological lenses. This is not the syncretism of evolutionary plagiarism, but the subversion of worldview polemics.
Buy the novel Noah Primeval, here on Amazon.com in Kindle or paperback. The website www.ChroniclesOfTheNephilim.com has tons of way cool free videos, scholarly articles about Watchers and Nephilim Giants, artwork for the series, as well as a sign-up for updates and special deals.
FOOTNOTES
1. Gordon J. Wenham, “The Coherence of the Flood Narrative,” Vetus Testamentum 28, no. 3 (1978), p. 346.
2. Alexander Heidel, The Gilgamesh Epic and Old Testament Parallels, Chicago, IL: University of Chicago, 1946, 1963, p. 230-232.
3. Heidel, The Gilgamesh Epic, pp. 232-236.
4. .R. George, The Babylonian Gilgamesh Epic: Introduction, Critical Edition and Cuneiform Texts, Vol. 1, Oxford University Press, 2003, pp. 518.
5. Heidel, The Gilgamesh Epic, p. 255.
6. George, The Babylonian Gilgamesh Epic, pp. 518.
Noah Facts #8: Noah Vs. Gilgamesh Smack Down!
Noah is a hot topic these days because of the movie with Russell Crowe. Here is some research I’ve done to add to that conversation.
I’ve written a Biblical fantasy novel called Noah Primeval. I’ve researched this topic extensively. Noah Primeval has been a category bestseller on Amazon for 3 years. It’s first in a series of novels called Chronicles of the Nephilim.
Did the Bible Copy the Flood Story from an Ancient Babylonian Epic?
With all the talk about Noah and the Flood, it is inevitable that the old issue would come up about how every culture around the earth has Flood legends. There are even stories like the Akkadian Atrahasis, the Sumerian Ziusudra and the Babylonian Epic of Gilgamesh that have elements exactly like the Biblical story of Noah.
So, what does all the similarity mean? Did the Bible copy it’s story of Noah from an older myth?
One of the most famous and fascinating myths that find correlations with Noah’s Flood is the Epic of Gilgamesh from Babylonia. Let’s take a look at this epic and see how it compares with the Bible’s story of Noah.
Noah and the Flood in the Epic of Gilgamesh
The Epic of Gilgamesh is about an infamous Mesopotamian king, Gilgamesh of Uruk, who was a giant and claimed to be two thirds god, one third human (Sound familiar?). It tells the story of how Gilgamesh hungers for meaning and significance and sets out on a journey to find eternal life.
Perhaps the most important connection that the Epic of Gilgamesh has to the Bible is in the presence of a Noah character and his story of the Great Deluge. At the end of Gilgamesh’s journey he seeks out a man Utnapishtim (our Noah) in a distant land because he’s heard Utnapishtim/Noah survived the Flood.
Gilgamesh figures he might wrest from Utnapishtim his secret of eternal life from the gods. But when he discovers that death is intrinsic to human existence and the special gift will never be granted to another human being, he returns to his beloved city of Uruk and finds his final fame in building the mighty walls and city, which will continue after he is long dead.
Scholars have written endlessly on this topic ever since the first translations of the account were available in the late nineteenth century. A comparison of the two stories yields some significant similarities that indicate a common origin, yet some even more significant differences that indicate divergent meaning.
But what about the Genesis story of Noah’s ark? While it is virtually unanimous among scholars that Genesis was written and edited over time using multiple sources, the more extreme view of this has been adopted by the scholarly establishment that has sought to divide the Old Testament, and in particular the Flood story, into contradictory sources that have been woven together from an older “Yahwist” source and a newer “Priestly” source, all with opposing agendas.
This radical view is falling from favor with the advent of literary and form criticism and because of the complete absence of manuscript evidence to support the remote speculation of such radical redaction. (1) What is coming more to light is the genius of composition that exists in the final canonical literary form that virtually defies categorizing of specific sources.
For example, Gordon Wenham has pointed out the complex literary poetic form of “chiasmus” used in the Flood narrative. Chiasmus is a kind of mirroring literary structure that builds the plot with increasing succession, to the middle of the story, where the thematic message is highlighted, only to conclude the second half of the story in a reflective reversal of the first half.
At the risk of overwhelming the reader, here is the literary structure of the Genesis Flood narrative as detailed by Wenham, emphasizing the superior originality of authorship over alleged source material. (2)
Early Biblical criticism tried to reduce the Biblical Flood narrative to a derivative of the Babylonian version, but that theory is now thoroughly discredited. (3) Archaeologist P.J. Wiseman uncovered the existence of a “toledoth” formula in the repeated Genesis phrase, “these are the generations of,” that indicates original source material of inscribed clay tablets rather than a hodgepodge of Yahwist, Priestly, and other contrary sources. (4)Whatever narrative congruity exists between the Bible and the Gilgamesh Epic, their genetic ties are not found in being a derivative of one another.
In my novel Gilgamesh Immortal, while I do write of Gilgamesh visiting Noah and his wife on a distant island, and I do have Noah tell Gilgamesh the story of the Flood, just as he does in the Epic of Gilgamesh, I bring a subversive twist to the scenario. The story that Gilgamesh inscribes onto clay and stone is not the one that Noah told him. Why? Because Gilgamesh is not a repentant follower of Noah’s god, Yahweh Elohim, the God of the Bible. So it would make sense that if he rejects the living God, he would reject the living God’s metanarrative and replace it with his own that would exalt himself or his biased religious construction. So the version we read in the Epic of Gilgamesh today is the deliberately fabricated version of a rebel against Yahweh.
So what is the storyline of the Flood in the original Gilgamesh Epic?
In Tablet XI of the epic poem, Utnapishtim, the Gilgamesh Noah, explains that because of some unexplained sin of man, the pantheon of gods decide to send a Deluge to kill all of mankind. But the god of the waters of the Abyss, Enki (or Ea) defies the decision and sneaks away to give a dream to Utnapishtim, a wealthy man who lives in the city of Shuruppak in Mesopotamia. Through the dream, he tells him to tear down his house and build a large boat to save “the seed of all living creatures.” He gives him the dimensions of the boat and instructions of how to build it.
Utnapishtim is to lie to his neighbors when asked about the large boat by explaining that he is going to move downstream to the city of Eridu. When he finishes the boat, he loads on it all kinds of animals as well as all his extended family members and some skilled craftsman.
The gods then start a storm of wind and rain, led by the storm god Adad, that devastates the land with such force, even the gods get scared and hide up in heaven like frightened dogs with their tails between their legs. The blowing wind and gale force downpour lasts six days and seven nights until “all the people are turned to clay.”
The boat finally runs aground on Mount Nimush, and after seven days, Utnapishtim lets out a dove to see if it can find a perch, but it does not and returns to him. He waits and sends a swallow, and then finally a raven that does not return, indicating enough dry land to get out of the boat.
Utnapishtim then offers a sacrifice to the gods, who “smell the sweet savour” and “gather like flies around the sacrificer.” But when the great god Enlil arrives, he is angry to discover Utnapishtim survived the destruction. When he finds out that Enki had leaked the plan to Utnapishtim, they quarrel. But the crafty Enki denies violating the will of the gods because he did not tell Utnapishtim directly, but through a dream.
Enlil resigns himself to the trickery and decides to bestow immortality on Utnapishtim and his wife, so they would be like the gods, but placing them “at the mouth of the rivers” to dwell faraway from normal mankind.
Utnapishtim then explains to Gilgamesh that the gods will not assemble for his benefit to bestow upon him eternal life. He is destined to die like all humanity. To prove the impossibility, Utnapishtim tells Gilgamesh to stay awake for six days and seven nights to prove his worthiness of becoming immortal by exercising power over the stepchild of death: sleep. Gilgamesh cannot do so and he is sent on his way with the consolation prize of finding a magic plant that will restore his youth. As stated before, the serpent then steals that plant away from him.
So, what’s the deal? How does Gilgamesh compare with Genesis? You’ll have to wait until my next post to find out.
Buy the novel Noah Primeval, here on Amazon.com in Kindle or paperback. The website www.ChroniclesOfTheNephilim.com has tons of way cool free videos, scholarly articles about Watchers and Nephilim Giants, artwork for the series, as well as a sign-up for updates and special deals.
FOOTNOTES
1. See Umberto Cassuto, The Documentary Hypothesis and the Composition of the Pentateuch, Skokie, IL: Varda Books, 1941, 2005; Duane A. Garrett, Rethinking Genesis: The Sources and Authorship of the First Book of the Pentateuch, Baker, 1991; John H. Sailhamer, The Meaning of the Pentateuch: Revelation, Composition and Interpretation, Downers Grove, IL: Intervarsity, 2009; “The New Literary Criticism,” Gordon J. Wenham, Vol. 1, Genesis 1–15. Word Biblical Commentary. Dallas: Word, Incorporated, 1998, pp. xxxii-xlii; Victor P. Hamilton, The Book of Genesis, Chapters 1–17. The New International Commentary on the Old Testament. Grand Rapids, MI: Wm. B. Eerdmans Publishing Co., 1990, pp. 12-38.
2. Gordon J. Wenham, “The Coherence of the Flood Narrative,” Vetus Testamentum 28, no. 3 (1978), p. 338.
3. Bill T. Arnold and David B. Weisberg, “A Centennial Review of Friedrich Delitzsch’s ‘Babel und Bibel’ Lectures,” Journal of Biblical Literature, Vol. 121, No. 3 (Autumn, 2002), pp. 441-457.
4. P. J. Wiseman, D. J. Wiseman, Ed., Ancient Records and the Structure of Genesis: A Case for Literary Unity Thomas Nelson, 1985.
Noah Facts #7: The Sequel To The Days of Noah –– Jesus Kicks Angelic Butt
Just adding some discussion to the conversation about Noah that has been raised with the soon to be released Noah movie.
I’ve written a Biblical fantasy novel called Noah Primeval. I’ve researched this topic extensively. Noah Primeval has been a category bestseller on Amazon for 3 years. It’s first in a series of novels called Chronicles of the Nephilim.
Buy the novel Noah Primeval, here on Amazon.com in Kindle or paperback. The website www.ChroniclesOfTheNephilim.com has tons of way cool free videos, scholarly articles about Watchers and Nephilim Giants, artwork for the series, as well as a sign-up for updates and special deals.
The Watchers From the Flood are in Hades and Christ Proclaims His Triumph Over Them
1 Peter 3:18–22
For Christ also suffered once for sins, the righteous for the unrighteous, that he might bring us to God, being put to death in the flesh but made alive in the spirit, in which he went and proclaimed to the spirits in prison, because they formerly did not obey, when God’s patience waited in the days of Noah, while the ark was being prepared, in which a few, that is, eight persons, were brought safely through water… Jesus Christ, who has gone into heaven and is at the right hand of God, with angels, authorities, and powers having been subjected to him.
In my previous post, We looked at how this passage spoke of the spirit of Jesus, during the three days he was dead, proclaiming to the imprisoned spirits who were the rebellious Watchers and their evil minions from the Days of Noah. Those were the Sons of God who mated with the daughters of men. I hinted that this journey of Christ’s was a descent into Hades or Sheol. I explained the ancient concept that assumes earthly rulers and powers are animated and empowered by spiritual or cosmic rulers and power behind them.
But where exactly are the angels imprisoned? And what exactly did Jesus “proclaim” to them? The answers are amazing.
Where is the “Prison”?
One interpretation of the prison is that it is a metaphor for human beings on earth who are “imprisoned” in their sin. But the context of the passage mitigates against this view. When the New Testament refers to preaching the Gospel to people on earth, the Greek term for “soul,” is used (psyche). But this is not a term about a ghost in a machine, but rather an expression of the life of an individual human, their inner being, their “person,” or their “self.”
Peter writes in 3:20 that “eight persons (psyche) were brought safely through the waters” in the ark during the Flood. When Peter preaches the Gospel in Acts 2, it says that “those who received his word were baptized, and there were added that day about three thousand souls [psyche]… and awe came upon every soul [psyche]” (Acts 2:42-43). “Soul” could be used synonymously with “individuals” or “persons.”
But in 1 Peter 3, the distinct Greek term for “spirit” (pneuma), not “soul” (psyche), is used in contrast to the physical flesh. And these “spirits” are those who were disobedient in the days of Noah (v. 20), so they could not be people on earth at the time of Christ. Christ was proclaiming to spirits. During the time of Christ, those who were around in the days of Noah could only be in one place according to the Old Testament: The Underworld of Hades or Sheol.
Hades was well known in the Greco-Roman world as the holding cell of the spirits of the dead until the judgment. Sheol was the Hebrew equivalent for Hades so the two could be used interchangeably. Prisons in that time period were exactly that, holding cells for punishment. So when Peter refers to a prison for spirits, this view concludes that he is referring to Hades/Sheol, just as he did in 2 Peter 2:4 when he said that the disobedient angels were cast into Tartarus, the lowest point in Hades.
The descent of Christ in 1 Pet. 3:19 is poetically structured to counterbalance the ascent of Christ into heaven in verse 22. In the same way that Christ went down into Hades, he later ascended up into heaven. But more importantly, if Christ makes a proclamation to the spirits in prison, those dead and bound prisoners are certainly not in heaven. They are most likely in Hades.
Another passage, Ephesians 4:8 quotes Psalms 68:18 about Christ “ascending on high and leading a host of captives.” Paul then adds a parenthetical,
Ephesians 4:9-10
“In saying, ‘He ascended,’ what does it mean but that he had also descended into the lower regions, the earth? He who descended is the one who also ascended far above all the heavens, that he might fill all things.”
Christ “descending into the lower regions, the earth” can legitimately be interpreted as referring to Christ’s incarnation or even his descent in the Spirit on Pentecost. But other scholarship argues that the phrase is better translated as “descending into the lowest parts of the earth,” in other words into Hades. (1)
This Underworld interpretation would seem to coincide with the memes presented in 1 Peter 3. The contrast of the heights of heaven with the depths of Hades, and the tying of Christ’s death, descent into Hades, resurrection, and ascension into the totality of his victory over the angelic principalities and powers.
Psalm 68 says that after leading the host of captives, God “received gifts from men,” a reference to the notion of ancient victors receiving tribute from their conquered foes. Paul changes that “receiving of gifts” into “giving of gifts” as a expansion of that victory over foes into a sharing of victory with his army, the people of God. But the context of conquest over the angelic powers is also apparent in Eph. 1:20-21, “when he raised [Jesus] from the dead and seated him at his right hand in the heavenly places, far above all rule and authority and power and dominion, and above every name that is named.”
Christ’s death on the Cross becomes the apparent defeat by God’s enemies, led by angelic principalities and powers. But it turns around and becomes a disarming of those spiritual powers and the beginning of his triumph over them (Col. 2:15). In this view, Christ dies, goes down into Hades to make a proclamation to the original minions of evil, now held captive. Then he raises from the dead and ascends into heaven to be coronated as king over all authority and powers of heaven and earth (Eph. 1:20-21). And that victory over spiritual powers brings us to the next element of 1 Peter 3:18-22.
What was the Proclamation?
In the ancient world, kingly victors would perform a triumphal procession through the streets of a conquered city. They would parade their captive opponents, alive or dead, on carts to show off their power over their enemies. Thus the triumphal procession in Psalm 68 quoted in Ephesians 4:8 as “ascending on high and leading a host of captives.” This would also be an encouragement for obedience from the vanquished inhabitants. (2) Triumphal language like this in 1 Peter as well as other passages (2 Cor. 2:14; Col. 2:15), reflect this military type victory of Christ over the ruling authorities achieved at the Cross.
This triumph is referred to in the next verse of 1 Peter 3:22. “Christ, who has gone into heaven and is at the right hand of God, with angels, authorities, and powers having been subjected to him.” The subjection of the spiritual powers occurs sometime before or during the ascension in this passage, most likely in the prison of Hades.
In Col. 2:15 we read that God “disarmed the rulers and authorities and put them to open shame, by triumphing over them” in Christ’s death and resurrection. Messiah’s death on the cross forgives us the legal debt of our sin, and his resurrection unites us in a new spiritual life.
But why would Christ have to proclaim authority or victory to those who were already imprisoned? Would that not be anti-climactic? Not if their fellow fallen angelic powers still ruled outside that prison on the earth, much like imprisoned Mafiosa leaders are still linked to their fellow criminals on the outside.
The angelic powers imprisoned at the Flood were the original rebels, the progenitors of the ongoing Seed of the Serpent that continued on in a lineage of evil on earth. They were in bonds, but the resultant War of the Seed that they spawned originated with their fall.
Christ’s death, resurrection and ascension secured his victory over the principalities and powers and gave him all authority with which to draw the nations back to him through the Good News of his kingdom.
Buy the novel Noah Primeval, here on Amazon.com in Kindle or paperback. The website www.ChroniclesOfTheNephilim.com has tons of way cool free videos, scholarly articles about Watchers and Nephilim Giants, artwork for the series, as well as a sign-up for updates and special deals.
FOOTNOTES
1 “κατώτερος,” Gerhard Kittel, Geoffrey W. Bromiley, and Gerhard Friedrich, eds., Theological Dictionary of the New Testament (Grand Rapids, MI: Eerdmans, 1964–), 640; Clinton E. Arnold, Zondervan Illustrated Bible Backgrounds Commentary: Romans to Philemon., vol. 3 (Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan, 2002), 325.
2 Clinton E. Arnold, Zondervan Illustrated Bible Backgrounds Commentary: Romans to Philemon., vol. 3 (Grand Rapids, MI: Zondervan, 2002), 387.
Noah Facts #6: The Days of Noah and How Jesus Fits In
 Special thanks to Darren Aronofsky and Paramount for raising the discussion of Noah with the new movie.
Special thanks to Darren Aronofsky and Paramount for raising the discussion of Noah with the new movie.
Buy the novel Noah Primeval, here on Amazon.com in Kindle or paperback. The website www.ChroniclesOfTheNephilim.com has tons of way cool free videos, scholarly articles about Watchers and Nephilim Giants, artwork for the series, as well as a sign-up for updates and special deals.
•
•
•
Christ’s Descent Into Hades/Sheol
One of the most difficult and strange passages in the New Testament is 1 Peter 3:18-22. It’s oddity is only matched by the fact that it is connected to another difficult and strange passage in the Bible: Genesis 6:1-4. The Genesis passage speaks of the Sons of God mating with the daughters of men in the days of Noah and breeding Nephilim giants that lead to the judgment of the Flood.
1 Peter 3 is notorious for its difficult obscurity and lack of consensus among scholarly interpretation. Views are divided over it with a variety of interpretations to pick from. So, let’s take a look at it more closely with an attempt to clarify its meaning.
1 Peter 3:18–22
For Christ also suffered once for sins, the righteous for the unrighteous, that he might bring us to God, being put to death in the flesh but made alive in the spirit, in which he went and proclaimed to the spirits in prison, because they formerly did not obey, when God’s patience waited in the days of Noah, while the ark was being prepared, in which a few, that is, eight persons, were brought safely through water… Jesus Christ, who has gone into heaven and is at the right hand of God, with angels, authorities, and powers having been subjected to him.
When Did Christ Go on His Journey?
Some believe it was after Christ was resurrected in his body that was “spiritualized” by the Holy Spirit. The oldest most traditional view was that this occurred when Christ was dead. It was his “living spirit” that is being contrasted here with his “dead flesh” on the cross or in the grave. But whether Christ proclaims in his resurrected body or in his immaterial spirit, the next question arises, who are the spirits to which he proclaims and where are they? This will help clarify the picture.
Who are the Spirits in Prison?
The identity of the spirits has been debated extensively and falls into four possible categories: Human spirits, demons, fallen angels, or a combination of the above.
John Elliot debunks the notion that “spirits” refers to human beings by looking at the Greek word for spirits (pneuma) in Biblical and Intertestamental texts. He concludes, “use of ‘spirits’ for human beings is very rare, and even then it is always qualified. In the Bible and related literature, when reference is made to deceased humans in Hades or the underworld, the term used is not pneuma but psyche.” (1)
But another commentator, Ramsey Michaels, shows that “spirits” (pneuma) is used of demons frequently in the New Testament for those supernatural beings that Jesus often confronted in his ministry. (2) He points out that in 1 Enoch (a likely source text for this passage), pneuma is used of both the giants and demons as the surviving part of the giants killed in the Flood.
1 Enoch 15:8-10
But now the giants who are born from the (union of) the spirits and the flesh shall be called evil spirits upon the earth, because their dwelling shall be upon the earth and inside the earth. Evil spirits have come out of their bodies.
But what of the fallen angelic Sons of God (also known as Watchers)? Are they ever referred to as “spirits”? As the 1 Enoch 15 passage above shows, the spirits of the Nephilim hybrids comes from their angelic Watcher progenitors who are also called spirits. In verse 4 of that passage, Enoch condemns the Watchers for violating their heavenly being as spirits (pneuma) and defiling themselves with “the blood of the flesh begotten children.” (3)
The only other New Testament Scriptures that speak of imprisonment of spirits are Jude 6 and 2 Peter 2:4, the very passages that are literarily dependent on the book of 1 Enoch. (4)
Jude 6 (NASB95)
And angels who did not keep their own domain, but abandoned their proper abode, He has kept in eternal bonds under darkness for the judgment of the great day
2 Peter 2:4
God did not spare angels when they sinned, but cast them into hell [Tartarus] and committed them to chains of gloomy darkness to be kept until the judgment…
1 Enoch 12:4; 10:12
the Watchers of heaven who have abandoned the high heaven, the holy eternal place …bind [the Watchers] for seventy generations underneath the rocks of the ground until the day of their judgment.
Jude not only quotes Enoch outright in Jude 4, but throughout his entire letter, he follows the progression of ideas in 1 Enoch and references memes and motifs from that ancient source text. 2 Peter 2 is considered a paraphrase of Jude with the addition of the word for Tartarus as the description of the location of punishment.
Tartarus was well known by the ancients as the lowest place of the Underworld where the Titans were bound in pagan mythology. That Underworld was referred to as Hades (Greek) or Sheol (Hebrew), and has obvious conceptual links to Jude and Peter’s location of punishment (see below for more on Tartarus and Hades). (5) It would make most sense that Peter’s second letter about angels bound in the prison of Tartarus would have continuity with the “spirits in prison” he is writing about in this first letter.
But the spirits are specifically indicated as being those who were disobedient during “the days of Noah while the ark was being prepared.” That “days of Noah” is exactly the time period that 1 Enoch speaks of the fallen Watchers and their giant progeny receiving their comeuppance with a binding in Tartarus/Hades at the Flood.
1 Enoch 10:11-13
And to Michael God said, “Make known to [the angels] who fornicated with the women…bind them for seventy generations underneath the rocks of the ground until the day of their judgment and of their consummation…in the prison where they will be locked up forever.
Chad Pierce makes a convincing argument that the disobedient spirits are not just the Watcher angels, demons, or human spirits alone, but the sum total of all who defied God at that time because cosmic powers are often united with human powers in the ancient world. (6)
In the Bible, the angelic power over Persia animated the human kingdom of Persia (Dan. 10:13), The Roman human kingdom in Revelation is granted its power from Satan (Rev. 12-13), and both are destroyed together in the Lake of Fire (Rev. 19:20; 20:7-10).
Wink explains that the ancient mind of the Biblical writers was steeped in a macrocosm/microcosm of “what is above is also below.” “Angelic and demonic activity in heaven was reflected in events on earth…These Powers are both heavenly and earthly, divine and human, spiritual and political, invisible and structural.” (7)
Reicke adds that the “fallen Angels… the Powers, the demons in general, can in a certain way represent the whole world of fallen angels.” (8) It appears that the author of 1 Pet 3:18-22 has left the recipients of Christ’s message purposefully vague so as to include all forms of evil beings. The spirits in prison are thus all the forces of evil which have now been subjugated and defeated by Christ.” (9)
In the next post, I will take a look at just what did Jesus actually “proclaim” to these imprisoned spirits?
Buy the novel Noah Primeval, here on Amazon.com in Kindle or paperback. The website www.ChroniclesOfTheNephilim.com has tons of way cool free videos, scholarly articles about Watchers and Nephilim Giants, artwork for the series, as well as a sign-up for updates and special deals.
FOOTNOTES
John H. Elliott, 1 Peter: a New Translation with Introduction and Commentary (vol. 37B; Anchor Yale Bible; New Haven; London: Yale University Press, 2008), .
2 Matt 8:16; Luke 10:20; “unclean spirits” in Matt 10:1; Mark 1:27; 3:11; 5:13; 6:7; Luke 4:36; 6:18; Acts 5:16; cf. Rev 16:13; “evil spirits” in Matt 12:45//Luke 11:26; Luke 7:21; 8:2; Acts 19:12–13 (for the singular, cf. Matt 12:43//Luke 11:24; Mark 1:23, 26; 3:30; 5:2, 8; 7:25; 9:17, 20, 25; Luke 8:29; 9:39, 42; 13:11; Acts 16:16, 18; 19:15–16).” J. Ramsey Michaels, 1 Peter, vol. 49, Word Biblical Commentary (Dallas: Word, Incorporated, 1998), 207.
3 Charlesworth, The Old Testament Pseudepigrapha vol. 1, 21.
4 Nickelsburg, 1 Enoch: a Commentary, 7. Also, E. Isaac, “A New Translation and Introduction,” in The Old Testament Pseudepigrapha, vol. 1 (New York; London: Yale University Press, 1983); Robert Henry Charles, ed., Pseudepigrapha of the Old Testament, vol. 2 (Bellingham, WA: Logos Bible Software, 2004), 178.
5 See the Appendix of Brian Godawa, Enoch Primordial (Los Angeles, Embedded Pictures Publishing, 2013), 336-338.
6 Chad Pierce, Spirits and the Proclamation of Christ: 1 Peter 3:18-22 in Its Tradition-Historical and Literary Context, (Durham theses, Durham University, 2009), 215-218. Available at Durham E-Theses Online: http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/13/
7 Walter Wink. Naming the Powers: The Language of Power in the New Testament (The Powers : Volume One), (location1552-1553, 182-183.) Kindle Edition.
8 Bo Reicke, The Disobedient Spirits and Christian Baptism (New York: AMS Press, 1946), 121.
9 Pierce, Spirits and the Proclamation, 218. See also Reicke, The Disobedient Spirits, 121.